In the not-too-distant-past, you had two transmission types to choose from: manual and automatic.
Today, however, you also have DSG (direct shift gearbox) and CVT (continuous variable transmission) options.
But what is ‘DSG’ in cars? What about CVT transmissions? And how do these compare to manuals and automatics?
In this article we’ll discuss the key differences between DSG and CVT transmissions, and why you might choose one over established gearbox designs.

DSG vs Automatic transmission
A particular question in relation to this transmission type is often asked: Is DSG automatic?
The answer is an emphatic ‘yes’ - since the system requires zero input from the driver.
On the outside, direct shift gearboxes look just like automatic gearboxes: you have an accelerator and a brake, and you'll likely have Park, Reverse, Neutral and Drive settings.
However, the mechanics of a DSG are very different from a standard auto.
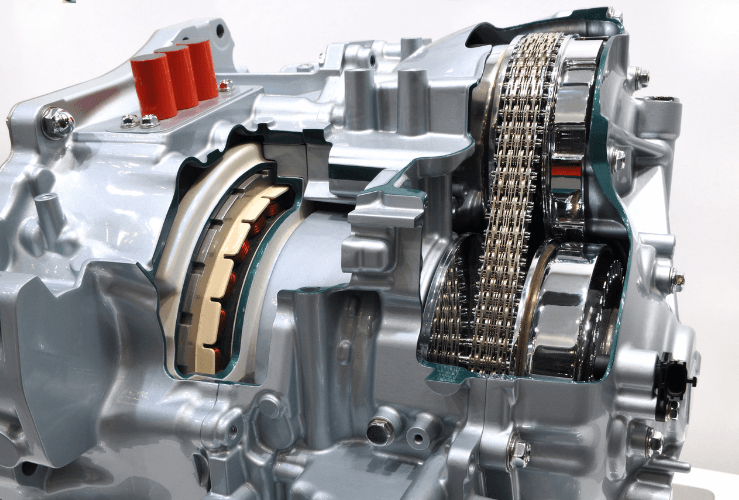
A DSG gearbox system essentially comprises two gearboxes, connected to the engine via two driveshafts. It also has two clutches.
A complex mechatronics system operates both the gearboxes and the clutches.
The primary benefit of a DSG over a regular automatic is that it can prepare the next likely gear change ahead of time, making for quicker and smoother gear changes.
Road speed, engine speed, accelerator position and drive setting are gathered in real-time to determine the optimum next gear and shift point.
How DSG Transmissions Work
A DSG (Direct Shift Gearbox) is a type of automatic transmission that combines the best of both worlds. Technically it’s two separate gear shafts—one for even gears and one for odd. Each shaft has its own clutch which allows the system to pre-select the next gear while still in the current one.
When a gear change occurs the clutches swap over almost instantly—resulting in super fast, seamless shifts with minimal power interruption. The dual-clutch system is managed by a clever mechatronic unit that monitors throttle input, road speed, engine load and more to select the best gear.
Because of this setup DSG gearboxes are known for their smoothness, quick response and efficiency over standard automatics.
Which cars feature a DSG gearbox?
DSGs are usually offered as an optional extra, and can cost in excess of £1,000.
Volkswagen Group has been a champion of the DSG gearbox system, offering it on models across their brands: VW, Audi, Skoda and SEAT. More recently, Ford, Hyundai and Kia, have started to embrace the technology - since it offers an easier, more pleasant driving experience, and in some cases better fuel efficiency.
But support for DSG automatics is not universal. BMW, for instance, recently moved away from its own DCG system (direct clutch system), and back to its single clutch automatic system. Improvements in their automatic gearbox technology has meant that gear change times are not far off those of the DSG system. They also managed to add another gear, improving efficiency.

DSG vs manual transmissions
With its computer-controlled gear changes, DSGs are considerably quicker than even the quickest manual driver.
With shifts taking a mere 8 milliseconds, they offer superfast, smooth gearshifts that human hand-eye coordination simply cannot match.
DSGs may also offer better fuel efficiency - although this may depend on the particular system and/or driving conditions.
The DSG also features engine braking, and is quicker from standstill.
Crucially, the DSG requires far less input from the driver - which on our increasingly congested roads, can make for less stressful, less tiring urban motoring.
However, since manuals have only one clutch system (compared to the DSG's two) they are simpler, less prone to failure - and therefore cheaper to maintain.
And for some motorists, a manual gearbox is more enjoyable that an automatic - this is because it offers the sense of control and allows the driver to better feel the acceleration of the engine.
As mentioned, the smoothness and efficiency of a DSG system could cost more than £1000 extra - which means the good old-fashioned manual transmission still has its appeal.
CVT vs DSG transmissions
What is a CVT gearbox?
A CVT - or continuously variable transmission - shifts between an endless range of gear ratios, quickly and seamlessly.
This compares to other transmissions - including the DSG - which has a fixed number of gear ratios.
CVTs are also known as single-speed, stepless, and shiftless transmissions.
Key advantages of the CVT are constant angular velocity, smooth acceleration and improved fuel economy.
Leonardo DaVinci invented the first CVT system way back in 1490 - with Daimler and Benz patenting their own version in 1886.
The CVT is similar to their DSG in that it delivers smooth gear changes and interrupted engine power.
However, the CVT harnesses belts and pulleys instead of fixed gears - which essentially means it operates more optimally than the DSG system.
CVTs are also more fuel efficient than both DSGs and regular automatics.
Manual vs automatic
Unsurprisingly, a manual gearbox is operated by the driver - manually - while an automatic moves through the gears - automatically.
A manual transmission features three pedals: an accelerator, a brake and a clutch.
The clutch must be depressed by the driver for gear changes to take place.
An automatic, meanwhile, only has two pedals: an accelerator and a brake. No human operated clutch is required since the gearbox manages the gear shifts.
Manual gearboxes are better at transferring power from engine to wheels, and offer faster acceleration. They are also simpler than automatics and so are less prone to failure.
The key advantage of the automatic is that it's less tiring to operate. If you do a lot of city driving, where start-stop traffic is the norm, an automatic transmission could make life a lot easier.
Advantages and Disadvantages of AMT
An Automated Manual Transmission (AMT) is a hybrid system that automates gear shifting in a traditional manual setup. It uses actuators and sensors to shift gears without the driver having to press the clutch pedal.
Advantages of AMT:
- Cheaper than DSG or CVT systems
- Better fuel efficiency than standard automatics
- Simpler design than dual-clutch systems
Disadvantages of AMT:
- Gear shifts can feel jerky or delayed compared to DSG
- Less refined than CVT or fully automatic systems
- Often only found in entry-level or budget cars
AMTs offer a balance of affordability and convenience but won’t deliver the same smoothness or performance as premium transmissions.
Market Trends in Gearbox Preferences
In the last few years automatics have gained massive ground in the UK. In 2011 only 24% of new cars had automatics. By 2021 that figure was 64% and the trend is set to continue.
Several factors are driving this change:
- More traffic congestion making automatics more appealing
- More DSG and CVT options available
- Hybrid and electric vehicles which use automatics by default
- Fewer manual driving tests and licences being taken by younger drivers. Manuals are still liked for their simplicity and fun but the trend is towards automatic, CVT and DSG for convenience.
In summary: Which gearbox is best for you?
Within the automatic bracket, DSG and CVT systems both offer super-smooth gear changes and minimal or zero driver input - and are both superior to regular automatics in most regards.
However, the more complex a system, the more liable to failure it can be - and the more costly to repair.
This is where the manual has a key advantage over its newer rivals: it is much cheaper to maintain. And for some drivers, it remains the most enjoyable transmission system.
That said, in a world where automation is becoming the norm, it is inevitable that the manual gearbox will make way for more advanced systems such as DSG and CVT.
Whether you drive an automatic, manual, or a car with a DSG or CVT To ensure peace of mind on the road, explore our comprehensive breakdown cover options at Start Rescue.
Frequently Asked Questions
The difference between DSG and automatic transmissions lies in how they shift gears. DSG gearboxes use two clutches and pre-select gears to shift faster and more efficiently.
That means you get smoother performance and better fuel economy compared to traditional automatics. That efficiency comes from the fact that DSG gearboxes can pre-select the right gear for the job.
CVT stands for Continuously Variable Transmission. It uses a belt and pulley system to deliver an infinite number of gear ratios meaning you get smooth acceleration and optimal engine performance.
CVTs are highly efficient and often used in hybrid and small-engine vehicles.
DSG and CVT have different strengths. DSG gearboxes are quicker to change gears and give you a more performance-oriented driving experience. That makes them particularly suited to sporty vehicles.
CVTs, on the other hand, prioritise fuel efficiency and seamless acceleration. Under normal driving conditions, CVTs are often smoother and quieter than DSGs.
Drivers tend to find DSGs more engaging—because of those quicker gear changes and the way they respond to your inputs.





